- Dapatkan link
- X
- Aplikasi Lainnya
- Dapatkan link
- X
- Aplikasi Lainnya
In light of this ORIF is indicated. Distal Clavicle Physeal Fractures are rare injuries to the distal physis of the clavicle in skeletally immature patients.

Acromioclavicular Joint Injury Shoulder Elbow Orthobullets
Drill the clavicle in a superior to inferior direction.

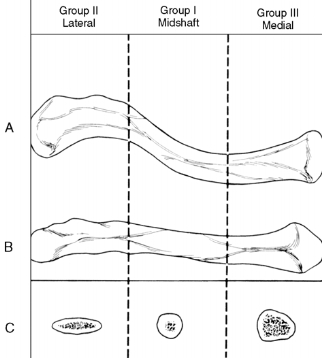
Clavicle fracture orthobullets. Clavicle Shaft Fractures are common pediatric fractures that most commonly occur due to a fall on an outstretched arm or direct trauma to lateral aspect of shoulder. Mechanism of injury. Midshaft clavicle fractures are common traumatic injuries seen in young adults that occur in the middle third of the clavicle.
Treatment is generally nonoperative management with a sling. Treatment decisions vary according to the fractures location and multiple classification schemes have been devised to describe fracture patterns. Type IIA and IIB and Type V fractures highlighted in red boxes below Type IV is non operative because it is a physeal fracture in pediatrics.
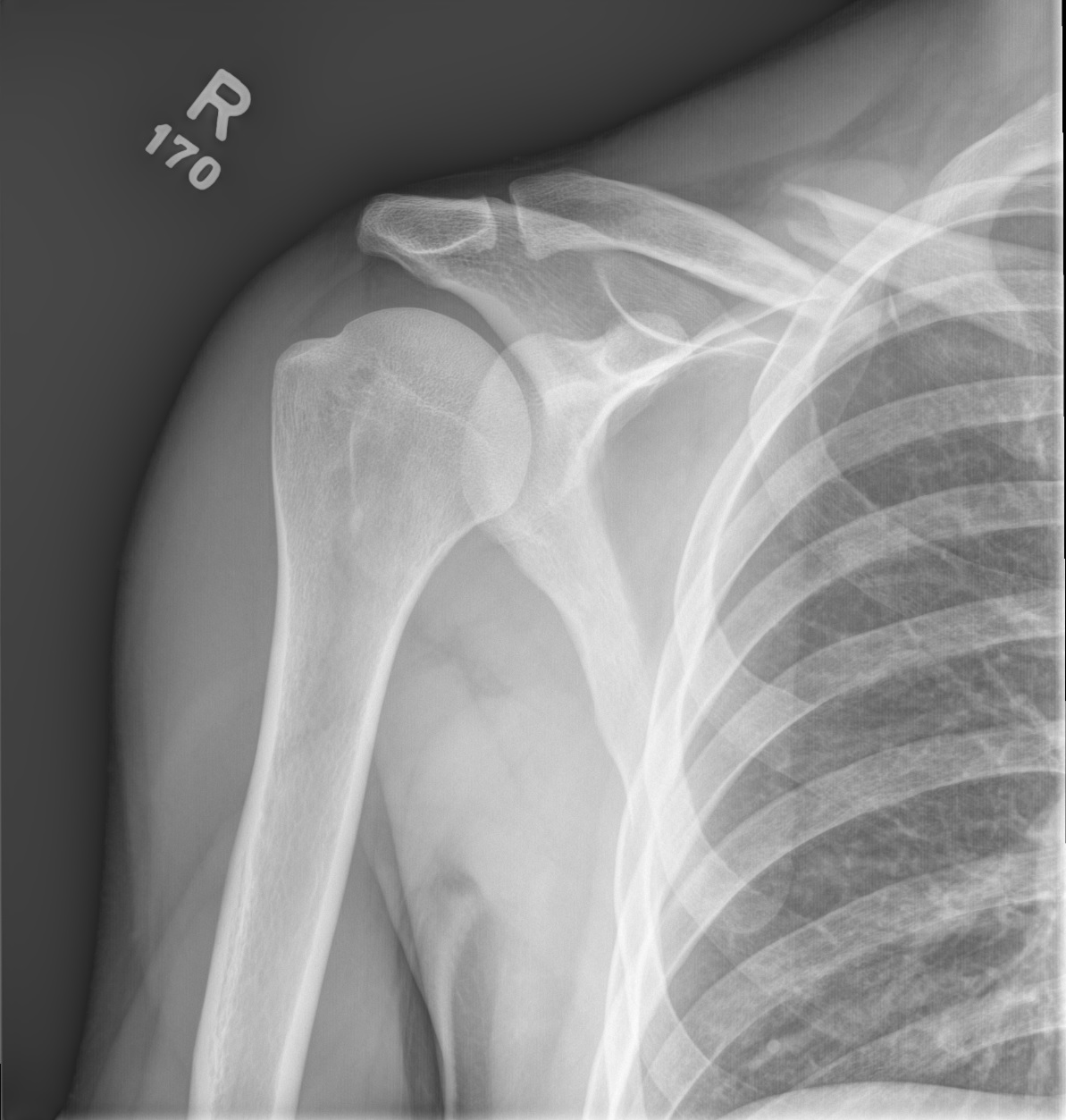
A clavicle fracture is a break in the collarbone one of the bones in the shoulder. Distal clavicle fractures are traumatic injuries usually caused by direct trauma to the shoulder from a fall in adults. Diagnosis can be made with plain radiographs.
Fracture line medial to coracoclavicular ligaments resulting in greater fracture displacement and higher incidence of nonunion. Spine fracture 29 Clavicle fracture 23 Brachial plexus injury 5 Associated Non-Orthopedic Injuries. A minimum of three screws should be placed bicortically in each major fragment of the fracture.
Place the plate anteriorly. An acromioclavicular joint injury otherwise known as a shoulder separation is a traumatic injury to the acromioclavicular AC joint with disruption of the acromioclavicular ligaments andor coracoclavicular CC ligaments. Most clavicle fractures occur when a fall onto an outstretched arm puts enough pressure on the bone that it snaps or breaks.
Partially remove the origins of the deltoid and the pectoralis major. The acromioclavicular AC joint remains intact. Pulmonary contusion 41 Head injury 34 Pneumothorax 23-32 Vascular injury 11 commonly axillary artery injury.
Fracture line runs between the intact conoid and trapezoid ligaments resulting in minimal fracture displacement. Distal Clavicle Physeal Fractures. Diagnosis can be made with plain serendipity radiographic views.
Medial Clavicle Physeal Fracture Clavicle Shaft Fracture - Pediatric Distal Clavicle Physeal FX Proximal Humerus Fracture - Pediatric. Diagnosis is made with bilateral focused shoulder radiographs to assess for AC and CC interval widening. Treatment is generally nonoperative management with a sling.
Prepare the fracture site. With the exception of the rare pathologic fracture due to metastatic or metabolic disease clavicle fractures are typically due to trauma Younger individuals often sustain these injuries by way of moderate to high-energy mechanisms such as motor vehicle accidents or sports injuries whereas elderly individuals are more likely to sustain injuries because of the sequela. Clavicle fractures are common injuries in young adults and children and diagnosis can often be made based on history and physical exam.
Treatment is controversial but may be nonoperative or operative based on patient activity demands and the degree of radiographic displacement and shortening. Operative treatment of these fracture is usually considered for open injuries and fractures with neurovascular compromise or overlying skin compromise 5 6. Medial Clavicle Physeal Fractures also known pseudodislocation of the sternoclavicular joint are rare injuries to the medial physis of the clavicle in children.
15 of clavicle fractures. Diagnosis is made with plain radiographs of the humerus and elbow. Illustration of the Neer classification of distal clavicle fractures.
Clavicle fractures are common injuries accounting for around 3 of all fracturesThey most commonly occur in adolescents and young adults however a second peak in incidence also occurs over the age of 60 associated with the onset of osteoporosis. Association with blunt aortic injury may be overestimated. Diagnosis can be made radiographically with shoulder radiographs.
Diagnosis is confirmed with standard shoulder radiographs and a 15 cephalic tilt view zanca view. CT scan is helpful for. Distal Humerus Fractures are traumatic injuries to the elbow that comprise of supracondylar fractures single column fractures column fractures or coronal shear fractures.
Diagnosis can be made with serendipity radiographic views but CT scan is the study of choice to differentiate from sternoclavicular dislocations. Place a LCP or precontoured plate on the anterior aspect of the clavicle. It is the most common fracture of childhood.
Clavicle fractures are very common injuries in adults 2-5 and children 10-15 and represent the 44-66 of all shoulder fractures. Type I fracture occurs distal to the coracoclavicular CC ligaments ie trapezoid conoid and involves minimal fracture displacement. Clavicular fractures can be classified by the Allman classification system determined by the anatomical location of the.
Displaced fracture medial to the conoid and trapezoid ligaments or separation of clavicle from the the ligaments. CT studies are generally required to assess for direction of displacement. Sternoclavicular Dislocations are uncommon injuries to the chest that consist of traumatic or atraumatic dislocations of the sternoclavicular joint.
Most medial clavicle fractures have traditionally been treated conservatively 1 3 4. Use depth gauge to measure the length of each screw. Diagnosis can be made with plain radiographs.
Type IIA fracture occurs medial to the conoid ligament. Drill the clavicle from an anterior to posterior direction. A clavicle fracture is also known as a broken collarbone.

Acromioclavicular Joint Injury Shoulder Elbow Orthobullets

Clavicle Shaft Fracture Pediatric Pediatrics Orthobullets

Clavicle Fracture Orthopedics Medbullets Step 2 3

Clavicle Anatomy General Features Osteology Attachments Development Clinical Anatomy Video Orthobullets

Neer Classification Type 1 Is A Fracture Lateral To The Download Scientific Diagram

Clavicle Shaft Fracture Pediatric Pediatrics Orthobullets
.jpg)
Clavicle Shaft Fracture Pediatric Pediatrics Orthobullets

Distal Clavicular Fractures And Acromioclavicular Dislocations Springerlink
Clavicle Fractures Non Op Or Surgery Ortho Conditioning
Clavicle Shaft Fracture Pediatric Pediatrics Orthobullets
Orthobullets Post Operative Radiograph Of A Clavicle Orif Facebook



Komentar
Posting Komentar